DLNA was created to facilitate the direct exchange of multimedia files between compatible devices over Ethernet or WiFi connections
You’ve undoubtedly seen these initials on some of the latest household gadgets, like hard disks, smartphones, desktop computers, and even television sets. The purpose of the DLNA standard is to make it possible to exchange multimedia content directly between compatible devices over a household Ethernet or WiFi network.
But what is DLNA connectivity?
DLNA refers to the concept of “Digital Living Network Alliance”, a standard created by a non-profit association of electronics and computer manufacturers that was established in 2003 by Sony, to promote the exchange of files, such as photos or videos, between smartphones, televisions, laptops and printers, over our home networks. Obviously, the electronic devices have to be compatible with this standard in order to offer, for example, the possibility of playing an MP3 stored on your smartphone on your stereo system, or watching a video stored on your laptop on your television.

However, it’s important to keep in mind that not all devices include this technology, and at this point, existing devices can’t be adapted. Nevertheless, you should know that you need to have a DLNA server and a DLNA client in order to transmit content using this standard.
Some companies, like Apple and Samsung, provide their own DLNA certificates, guaranteeing that you’ll be able to share multimedia files between their devices using the AirPlay and Samsung Link platforms. Others, like LG and Philips, have also joined the Digital Living Network Alliance with their respective exchange platforms SmartShare and SimpleShare.
How does DLNA work?
As we mentioned before, you need to have a DLNA server to store and transmit the multimedia files. These servers may be storage devices, laptops or multimedia servers for the home, like Serviio, Orb, TVersity or TwonkyMedia. Note that PCs with the Windows operating system already have DLNA incorporated into the system, and the Windows Media Player can act as the media server.
And, as we also mentioned, you also need to have a DLNA client if you want the file exchange over the home network to work. The clients are the devices on which the shared content is played, such as SmartTVs, stereo systems or printers.
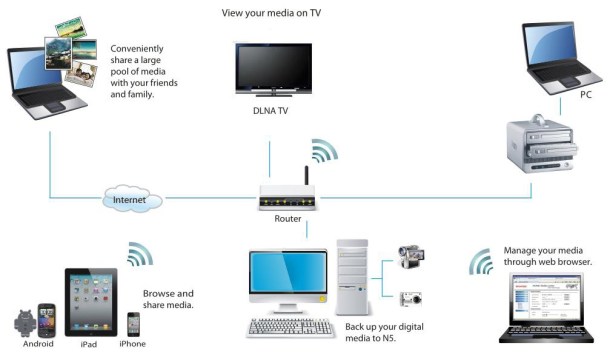
Thanks to the wireless communication of your WiFi or an Ethernet connection, you can play any multimedia file stored on a DLNA server using a DLNA client, but there are a few limitations in terms of file format that you need to bear in mind before synchronising two devices to play files.
Incompatibilities
One of the problems that you may run into when sharing content between your household devices is copyright restriction. DRM –Digital Rights Management– controls how people can share digital media and there may be some content that can’t be played on devices with DLNA certification.
Another common problem is the incompatibility of some devices when playing formats such as MP4 video or the popular DivX. However, some multimedia servers like TVersity can solve this problem by encoding content on the fly.